Reviewed December 2023
A recurring sequence specializing in plant cultivation by college researchers.
All crops require sure macro- and micronutrients to develop correctly and full their lifecycles. If considered one of these parts is missing or overapplied, plant development issues and tissue injury will happen, each above and beneath floor. When making use of these mandatory parts, it is very important hit the “candy spot”—the optimum degree for every nutrient. However wanting on the general nutrient ranges in your crop can also be vital. That is the place electrical conductivity (EC) is available in.
As we defined within the article, “Optimizing Electrical Conductivity (EC) in Hashish Cultivation,” in Hashish Enterprise Occasions’ April 2019 concern, “EC is {the electrical} cost that strikes by an answer. The upper the salt focus, the higher {the electrical} studying. The upper the focus of fertilizer salts within the answer or within the substrate, the upper the EC studying might be.” That article detailed monitor and handle EC. Whereas that’s important, your crops may also inform you when EC ranges are too excessive, and understanding the warning indicators might help you diagnose excessive EC.

Learn how to Take a look at EC Ranges
Most water-soluble fertilizers are comprised of a cation (ions that carry a constructive cost of their pure state) and an anion (negatively charged ions). These ions will dissolve and disassociate in water, so to measure the EC degree with an EC meter, {an electrical} cost from two diodes should cross by an answer. Like drawing traces from dot to dot, {the electrical} cost will “join” fertilizer ion to fertilizer ion till it reaches the opposite diode.
Whereas an EC studying will inform you what number of dissolved ions are in answer, it doesn’t establish every particular person component or the focus of every. For all crops, together with hashish, excessively excessive EC will end in plant injury (extra on this later).
Moreover, fertilization and irrigation strategies can impression the distribution and accumulation of the utilized fertilizer ions (Fig. 1).
With overhead or top-down irrigation, water motion within the pot will circulation downward to the underside of the container as a consequence of gravity, root uptake and evaporation occurring on the intersection of the substrate and air by the drainage holes. These three elements will trigger salt accumulation on the backside of the container, given that is the place water is evaporating and being taken up in its best portions. Thus, the basis injury might be best within the decrease portion of the substrate in top-down irrigation.
A easy visible inspection of the roots might help you establish the place the best root injury has occurred. Roots which can be clear or clear are wholesome, whereas roots that seem tan or brown could also be broken. This rule sometimes applies to hashish crops of their youthful and vegetative states. Bigger hashish crops and a few cultivars have darker roots, and bigger roots will usually be tan or brown as a consequence of lignification, or a pure hardening of cell partitions that happens in older crops. Root rot may even end in discolored roots.
The identical applies when irrigating from the underside or with sub irrigation, as properly, however is inverted. In sub irrigation or flood irrigation, the underside of the containers are flooded with a small amount of water. This water is then absorbed up into the pot by adhesion, cohesion, root uptake, evaporation and capillary motion. Thus, fertilizer salts will accumulate within the higher third of the basis ball or beneath the media floor.
When EC injury is suspected when utilizing sub or flood irrigation, look at the roots within the higher third of the pot for discoloration.

Visible Signs of Excessive EC
Signs of toxicity differ relying on crops’ age. We’ve described signs usually noticed by age beneath.
Preliminary Signs. Excessive EC injury signs will first seem within the decrease leaves and within the new and increasing rising suggestions (Fig. 2, prime of this web page). Harm begins there because of the manner vitamins transfer throughout the plant. The ions with the best portions in a high-EC answer are sometimes nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (Ok). Because the plant takes up extra water, it additionally takes up extra ions, that are dissolved in that answer. This can be a useful course of when vitamins are in stability; nevertheless, if the EC is just too excessive (i.e., there are too many dissolved ions), extreme tissue demise, or necrosis, will happen as a consequence of extreme uptake.
Youthful and Increasing Leaves. As famous earlier, signs of excessive EC will first develop and seem within the new and increasing leaves. These leaves are sometimes discovered on new development, whether or not on the ideas, aspect shoots, or inside branches, and at any stage. These areas are present process fast cell division and are absorbing quite a lot of water to totally develop and develop. Therefore, these areas would be the first to point out excessive EC signs. Signs that will floor amongst new development embody light-green coloration, and the margin (outer edges) of the increasing leaflets will flip brown (Figs. 2 & 3). This browning and leaf margin demise will proceed based mostly on the severity of the toxicity or focus of accrued fertilizer salts (excessive EC). If the EC may be very excessive, then these signs might be very extreme, and your complete leaf rising tip might flip brown and die.
Leaf Margin. The older and expanded leaves may even develop signs based mostly on excessive EC stress. These signs might seem along with the brand new and increasing leaves, or they might seem barely after. Very similar to the symptomology within the new and increasing leaves described on p. 26, the preliminary signs of excessive EC burn will seem on the leaflet margins. Browning and tissue demise will first seem on the leaflet margins and can progress inward towards the center of the leaf (midrib) and down towards the leaf base (towards the petiole) (Figs. 3 & 4). Hashish crops take up quite a lot of water when actively rising. The older leaves are very photosynthetically lively and thus will use extra water sources and accumulate the ions within the excessive EC answer sooner.
Superior Signs. If excessive EC options will not be mitigated, then extra salts will accumulate within the plant, particularly within the older, decrease leaves (Figs. 5 & 6). Because the leaves proceed to build up the ions, the leaflet margin will start to tackle a wilted look and can change into brittle and brown (necrotic). Finally, your complete leaflet will die, and solely the center of the leaf alongside the midrib might be inexperienced. If situations will not be corrected, your complete plant will die. Moreover, as a result of the plant just isn’t taking over as a lot water, a layer of salt crusting might seem on the substrate floor as a consequence of evaporation with any irrigation methodology (Fig. 7).

Correction and Prevention
The easiest way to make sure that excessive EC situations are prevented is to arrange a monitoring program so you may establish accumulating salts or fertility miscalculations early. Different articles we’ve written for CBT tackle arrange a monitoring program and carry out an in-house check on substrate pH and EC, and can information you on this course of. (For extra on this, learn the beforehand talked about “Optimizing Electrical Conductivity (EC) in Hashish Cultivation,” “Troubleshoot Hashish Nutrient Issues Earlier than They Happen,” and “New Analysis Outcomes: Optimum pH for Hashish.” Such exams embody the PourThru, 1:2 dilution, or saturated media extraction (SME). Checking the nutrient answer on the hose finish or drip emitter will assist decide if injector calibration is required, if injector failure has occurred, or if the fertilizer was miscalculated.
Submit Samples for Lab Testing
In-house monitoring of the EC provides a fast verify of your crop’s nutrient standing. One other useful gizmo is lab testing. Think about submitting periodic fertilizer answer samples to a industrial testing lab to find out your fertilizer answer’s dietary composition. This can be a nice strategy to decide the nutrient ranges offered by an natural fertilizer. Periodic water exams will present perception into your water high quality. Lastly, periodic substrate samples will assist you correlate your PourThru EC readings with the precise particular person component contribution of your fertilizer program.
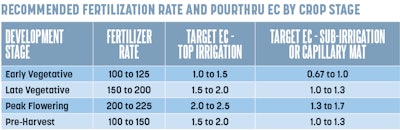
Corrective Procedures for Modifying Substrate EC
When the EC drifts into undesirable territory (Desk 1), changes should be made. Under are the usual corrective procedures used to change the substrate EC for greenhouse or indoor crops grown in soilless substrates and tailored for hashish.
1. Excessive Substrate EC Correction. If the EC is growing over time, this means the fertilizer is accumulating within the pot and the speed is larger than the demand by the plant. Step one can be lowering the fertilizer price to reasonable the buildup of fertilizer salts. (This additionally might help get monetary savings by not losing fertilizer answer.)
The second possibility is to irrigate the substrate twice with clear water to leach out the accrued fertilizer salts. This methodology is used when EC ranges are extraordinarily excessive to assist keep away from plant burn. (It additionally flushes away your fertilizer funding.) Monitoring the crop throughout manufacturing will assist to keep away from these elevated ranges within the first place and assist you get monetary savings.
2. Low Substrate EC Correction. On the alternative finish of the spectrum, if the degrees are decrease than the beneficial vary (Desk 1), this suggests the nutrient demand of the plant is larger than what’s being equipped. On this case, enhance the fertilizer price. One or two purposes of a better N price within the 250 to 400 ppm vary will increase the EC.

Conclusions
Excessively excessive EC ranges result in stunted development, leaf injury and ultimately plant demise. It’s best to keep away from this case by implementing in-house monitoring of the EC in your commonplace working procedures (SOPs), thereby establishing an everyday fast verify of the nutrient standing of your crop.
Dr. Brian Whipker is professor of floriculture within the Division of Horticultural Science at North Carolina State College. Paul Cockson is a graduate analysis and instructing assistant at NCSU. Patrick Veazie is an undergraduate researcher at NCSU. David Logan is an undergraduate analysis assistant at NCSU. Dr. W. Garrett Owen is an assistant professor and extension specialist of floriculture, greenhouse, and controlled-environment crop manufacturing within the Division of Horticulture on the College of Kentucky.






